Fast BGP Simulation of Large Datacenters
VMCAI 2019 (CCF B)
Nuno P. Lopes and Andrey Rybalchenko
1 | @inproceedings{lopes2019fast, |
[toc]
Background
outage 运行中断
misconfigurations, maintenance, upgrades, hardware and firmware failures -> production datacenters outage
| RIP | OSPF |
|---|---|
| DV | LS |
| Floyd | Dijkstra |
| OSPF | BGP |
|---|---|
| IGP | EGP |
| easily configured | complex |
| Dijkstra | Best path selection |
| Speed first | Best |
LS
- 链路状态路由算法
- 每个节点都周期性的向网络上所有其它节点广播自己到邻居节点的距离。每个节点都具有完整的网络信息,即知道网络上每条边的距离。于是,每个节点都可以彼此独立的使用Dijkstra最短路径算法来计算到网络上其它节点的最短路径。
边界网关协议 BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
- 一种实现自治系统AS(Autonomous System)之间的路由可达,并选择最佳路由的距离矢量路由协议
- 外部网关协议 EGP (Exterior Gateway Protocol): 在 AS 之间动态交换路由信息,只发布网络可达,不优选,不考虑环路避免等问题
- 路由优选、避免路由环路、更高效率的传递路由和维护大量的路由信息
- 角色
- Speaker: 接收或产生新的报文信息,并发布(Advertise)给其它BGP Speaker
- Peer: 相互交换报文的Speaker之间互称对等体(Peer)。若干相关的对等体可以构成对等体组(Peer Group)
- 报文
- Open报文:用于建立BGP对等体连接
- Update报文:用于在对等体之间交换路由信息
- Notification报文:用于中断BGP连接
- Keepalive报文:用于保持BGP连接,周期性发送
- Route-refresh报文:用于在改变路由策略后请求对等体重新发送路由信息。只有支持路由刷新(Route-refresh)能力的BGP设备会发送和响应此报文

- RIB (route information base)
- 维护每种协议的网络拓扑和路由表。这将包括许多到达相同目的地前缀的路由。
- FIB (forwarding information base)
- 是从下推的RIB中可能的许多协议到快速转发查找内存的最佳路径的最佳路由。
FASTPLANE - based on Dijkstra
- is two orders of magnitude faster than the state-of-the-art on small and medium datacenters (快两个数量级)
- goes beyond the state-of-the-art by scaling to large datacenters
静态检查无法处理一些路由器固件层面上的bug,因此需要用动态的模拟来寻找问题
总结:提出了一种快速可拓展的BGP系统模拟算法,它需要数据中心路由策略有单调性,用路由报文而非权重计算出单源最短路。
Datacenters and BGP
ASN (autonomous system number)
路径属性的词典顺序(这里用的是ASN) 替代 跳数
RIB根据配置初始化,根据新收到的前缀和unreachable更新
Illustration
Prefix Interaction
(router,prefix,AS path) 代表要到达 router,下一跳 prefix,中转路径 AS path
WL 中不止一个时,选择优先级最高的 (we need to visit a most preferred advertisement first)
优先级由 BGP 最优路径选择算法得出,即更短的 AS path 优先级更高。但并不总是可以比较的
- 算法被用于单路由?而FASTPLANE被用于处理属于不同路由的报文
- AS path length 可能相等
最终优先级先判断路径长度,在长度相同时选择 ASN 小的 (an auxiliary lexicographic order on names of routers)
路由根据自己是否已经在 AS path 中来决定是否要 reject 收到的报文
R2 此时 RIB 中不空且 24 > 16,进行 aggregation,生成新的 a'' = (R2, 10.0.0.0/16, <>) 作为种子
最后将 RIB 中每个前缀的最优报文交给 FIB
Globally vs. Locally Preferred Advertisements
当同一路由出现两个甚至多个竞争的报文时,选取并替换 WL
为什么 R4 就会等 R1 发的包呢?(by propagating only globally optimal advertisements)
Necessity of Monotonic Increase of Preference
FASTPLANE 需要路由节点的优先级越来越低 (the preference of a route advertisement at the destination router cannot be higher than the preference of the originating advertisement at the source router),但是又要求单调增???(ensure monotonic increase of preference)
最终优先级的判断修改为先判断配置中的优先级 local pref,再判断路径长度,最后在路径长度相同时选择 ASN 较小的一个 (the adver- tisement with the highest local preference is preferred. If advertisements have an equal value of the local preference attribute, then the advertisement with the shortest AS path is preferred)
(router,prefix,local pref,AS path)
Future Work
本文提出了一种计算路由表的算法,该算法仅适用于使用BGP的特定特征子集。需要进一步重新搜索,以拓宽和准确描述哪些特征集合(或多组)可以一起使用,并且仍然与拟议的算法(或类似的单调推理方法)兼容。
双重而言,需要进一步研究来描述要避免的协议功能,以支持高效的验证。此外,对是否/如何用单调特征取代非单调特征知之甚少。这不仅可以提高网络验证的效率,还可以加快生产网络的融合时间,因为撤回的广告会更少。
另一个途径是研究控制平面上的非确定性。有时不是总顺序,这意味着网络中可能存在不同的稳定状态。这有缺点,例如使故障排除变得更加困难。我们目前的原型故意以一致、确定性的方式计算单个稳定状态,以便结果可以重现。然而,这种稳定状态可能与真实网络稳定的状态不同。
Problem
第一个例子中RIB初始化后,如果R1和R3都为
10.0.0.0/24,R2应该怎么办- 对于相同的前缀长度,incomparable -> pick either of them arbitrarily
- 挨个运行?
遍历种子列表、prefix 选择等过程像是由主节点选择
- 猜测报文在每一步都返回到单源路由,由单源路由计算后再发出下一步?
计算单源最优路径,计算过程是由路由计算异步传播还是有中心计算并将结果给路由节点
- 节点自行计算
- By running BGP each datacenter router participates in a distributed best path computation, where information about the best paths is ex- changed between direct neighbors
- transBGP函数的OutRouteMap返回值和InRouteMap
- 节点自行计算
三个示例中修改使得非最优路径会提前发送
- 在后文中看到好像是会撤回后续节点RIB中的非最优路径,保留出现最优路径歧义节点RIB中的存储
only deal with transBGP that is monotonically increasing,增 or 减?
- In a network, monotonicity implies that the weight of a walk does not decrease when it is extended by a new link (Paper: An Algebraic Theory of Dynamic Network Routing)
初始状态多个路由器的配置有冲突,且交叉点有距离
- 4.4
Appendix
Reference
Slide
Batfish
ACLs and firewalls
Analysis Access Control Lists (ACLs) and Firewall Rules are permitting and denying traffic as intended.
- manually checking these rules
- loading them onto a lab device in order to test behaviors on example packets of interest
->
- time consuming
- error-prone
Batfish
- testfilters
- find how a given flow is treated
- searchfilters
- get guarantees for large spaces of flows
- filterLineReachability
- find unreachable lines
Provably Safe ACL and Firewall Changes
- block access to critical services
- expose sensitive resources
Batfish
- Ensure that the intended traffic is not already permitted
- searchfilters: permit or deny
- Ensure that the intended traffic is permitted in the candidate change
- Ensure that no collateral damage has occurred
- nothing but the intended traffic is impacted by the candidate change
- Step 2 again
- Step 3 again
Routing
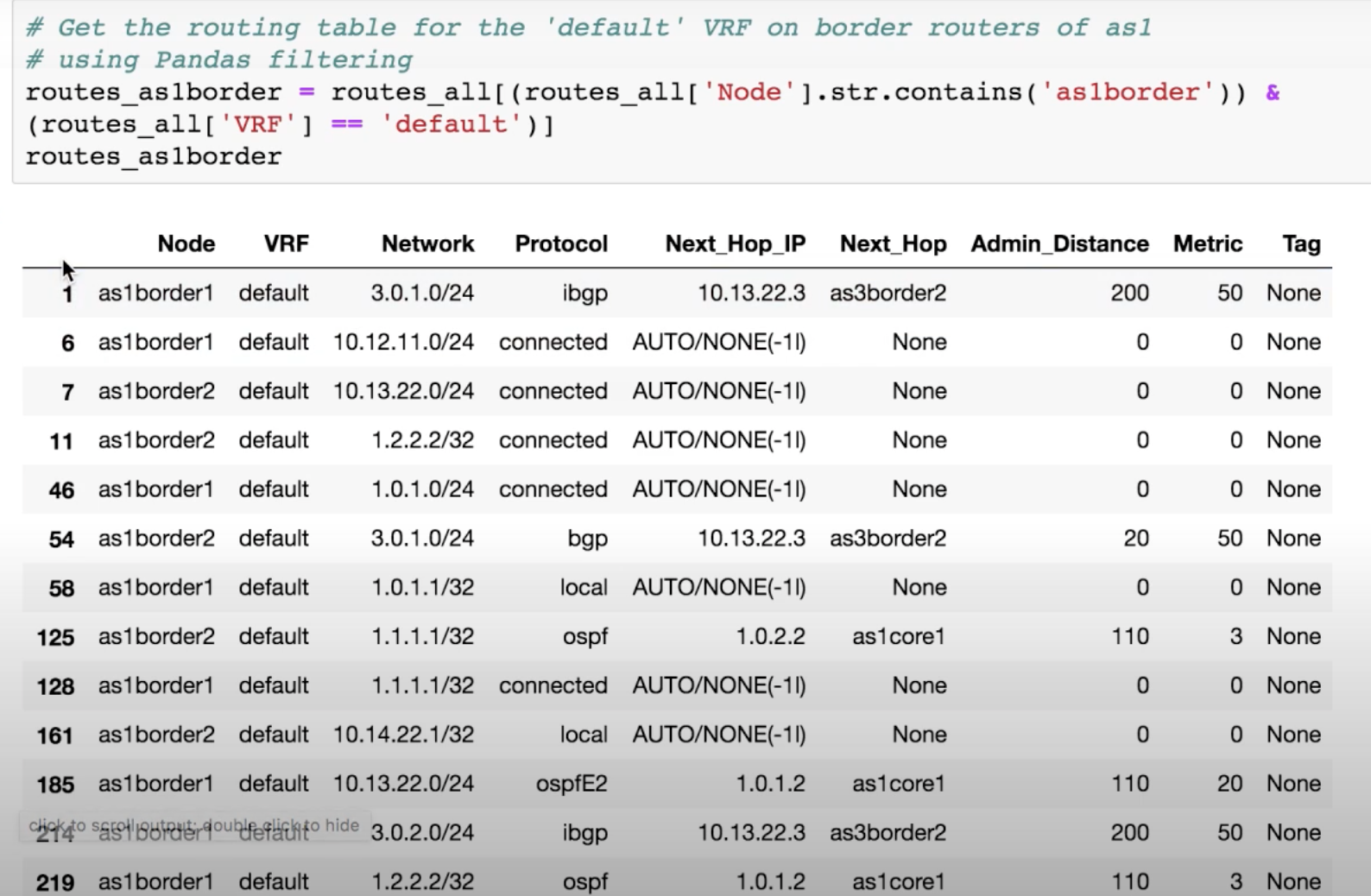
With Batfish and Pandas you can easily retrieve the exact information you are looking for from the routing tables on ANY or ALL network devices for ANY or ALL VRFs.
This concludes the notebook. To recap, in this notebook we covered the foundational tasks for route analysis:
- How to get routes at all nodes in the network or only at a subset of them
- How to retrieve routing entries that match a specific protocol or metric
- How to find which nodes have an entry for a prefix or which ones do not
Deep Thinking
在一个较大型的数据中心里,应该不会大量使用优先级来过多的影响报文的传播顺序。在本文这样的对于优先级数值单调性非常敏感的情况,可能在实际使用中只会在较为边缘的地方出现优先级不单调的节点配置。这样的话,示例3中的由于节点优先级变为200导致需要撤回已经发送的数据报文的情况就会少且影响范围不大。并且,通过作者举的三个例子可以看到,(如果我们将数据中心网络看作树形),FastPlane的运行流程可以视为一种BFS。由源路由节点作为根,在没有优先级变化的情况下相当于向外逐层拓展,层中根据字典序遍历。
1 | package main |
用Go简单表述一下意思。当出现优先级大于默认值100的报文(在这里以节点代替)时,就会出现此节点的抢占情况。由此节点作为根开始抢占运行新的BFS,原优先级的BFS将会在新BFS运行结束后继续运行。
由于是BFS,且出现非默认优先级通常处于较为边缘的位置,就会出现三种情况:
- 整个系统运行后期,出现高优先级报文
- 由于影响较小,仅需要撤回很少的错误报文,造成的额外开销也很小
- 整个系统运行初期,出现高优先级报文
- 直接以高优先级报文作为新的根开始BFS,从源节点到高优先级报文的节点路径不需要修改,其他节点路径由新的BFS决定
- 整个系统运行中期,在辐射网中间的边缘位置出现高优先级报文
- 影响较大
从刚才的表述中可以看到,如果说在系统运行前先找出非默认优先级的配置节点,先做由源节点到非默认节点的路径,然后再从此节点开始运行系统就可以。
仍需要考虑:系统中可能出现100、150、200等多个不同的优先级配置。尽管配置优先级时可以人为控制此因素,但是仍需要考虑100-150-200的初始路径,以及多个200的情况。